Symptoms of a food allergy might include rashes and trouble with the digestive system. When it incorrectly determines that a protein in the food poses a threat, your immune system will produce antibodies called immunoglobulin E. Histamine and other compounds are released into your blood as a result.
allergic rhinitis
Your immune system produces histamine when it detects an allergen, causing allergic rhinitis. Histamine swells the nose and throat cells, causing mouth, eye, lip, and throat itching. Itching is different from a cold or flu-related runny nose and sneezing because it doesn’t involve a temperature.
Before diagnosing rhinitis, the doctor will take a detailed history of your symptoms and when they occur. The doctor may also use skin tests to measure your reaction to tiny amounts of common allergens.

Fresh fruits, vegetables, nuts, and spices might cause hay fever in people because their proteins are identical to pollen proteins. This is cross-reactivity.
Asthma
Food allergies occur when the immune system reacts too strongly to innocuous proteins in foods. When an allergen is eaten, the immune system produces immunoglobulin E antibodies. These antibodies bind to two types of cells in the body that emit massive amounts of chemicals that induce tissue allergies.
Hives, itching of the mouth, throat, or skin (including palms, soles, and genitals), rashes, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, breathing difficulties, and anaphylaxis are possible symptoms. Anaphylaxis risk rises with age.

Research reveals that having one atopic disorder like hay fever or a food allergy raises the risk of asthma later in life. Atopic dermatitis commonly precedes asthma by a few years with food sensitivity.
IBS
IBS can result from food allergies. Gas, bloating, cramps, and stomach pain are symptoms. This chronic illness can be painful and affect people differently. It does not damage the bowel or raise the risk of cancer.
The way the small intestine processes FODMAP foods (fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols) may link IBS and food allergies. These are found in onions, garlic, and many fruits and vegetables.

You should inform childcare and school workers of your child’s food allergy. This helps individuals avoid allergic responses by knowing what to look for.
Eczema
Certain foods cause eczema flare-ups for many. Atopic dermatitis (eczema) may lower the skin barrier, allowing allergens to enter and eliciting an immunological response.
Food allergies that cause eczema can be found through allergy tests. Elimination diets, skin prick tests, and blood allergy tests are examples.
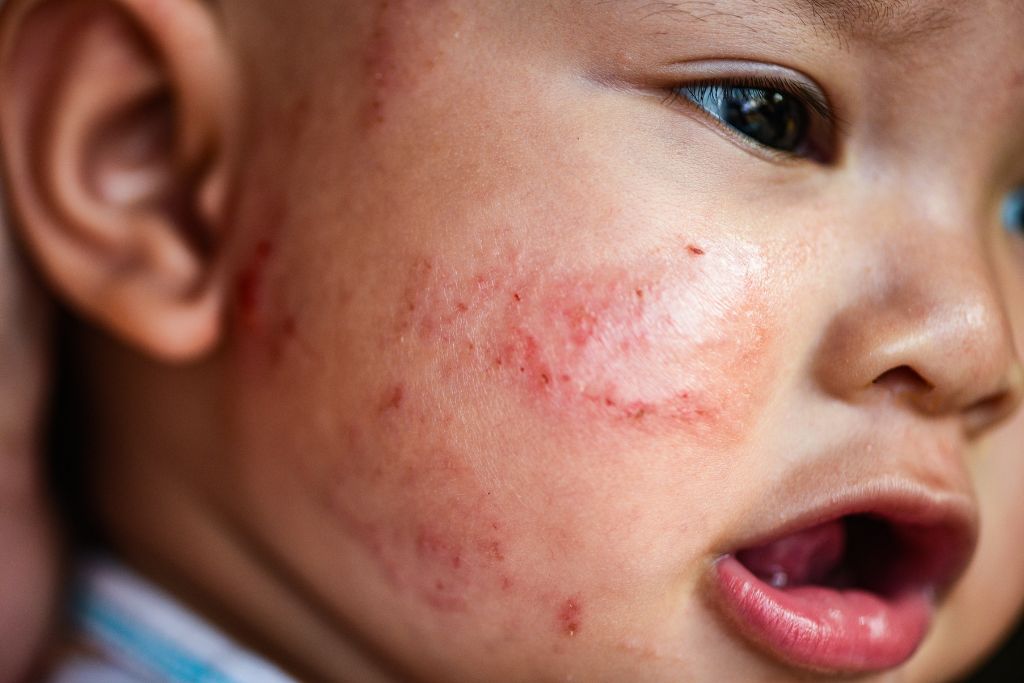
But people with eczema should avoid taking out whole food groups like eggs or dairy, which can cause other sensitivities and health issues. A doctor can help patients manage symptoms with a nutritious diet of fruits, vegetables, and non-dairy milk. Antihistamines can also relieve severe symptoms.
Hay fever
Food allergies release immunoglobulin E (IgE). Mast cells in the nose, lungs, skin, and digestive tract attach to it. Mast cells emit allergy-causing histamine and other substances.
Pollen, raw fruits, vegetables, soy, and tree nuts have comparable proteins, generating a cross-reaction. This is called pollen food syndrome or oral allergy syndrome. PFAS patients may feel itching in their mouth, tongue, and ears after consuming certain foods. The symptoms normally disappear after an hour.

Cooking certain meals or utilizing non-IgE-mediated food allergy medications can prevent PFAS. You must eliminate certain key nutrients from your diet. So check with a doctor to be sure you’re getting enough nutrition elsewhere.
Uncover the hidden connections between dietary sensitivities and various health conditions as discussed in “Food allergy can trigger THESE diseases.” Meanwhile, explore effective remedies for managing cold and cough symptoms naturally with insights from “Natural Cold and Cough Treatments That Work.” These articles offer valuable insights into the potential impacts of allergies on health and provide practical solutions for alleviating common ailments without relying on conventional medication.